NOTICE: Certain links on this post may earn a commission for Western Hunter Magazine from Amazon or our other affiliate partners when you make a purchase. Thank you for your support.
Navigating the Backcountry with Stock
Although there is a lot written about navigating the backcountry on foot both on and off-trail, there is very little information written about navigating in the backcountry with horses and mules, especially in hunting situations. In this article I will describe how I have traveled in remote areas throughout the West with my pack and riding stock, using both age-old techniques as well as the technology which is currently available to us today.
Be Prepared
A while back there was a 25-year-old Utah man on a horse packing trip with his father and two siblings who were lost in the Selway-Bitterroot Wilderness for five days before he was found, far off any trail. So far off that he had to be rescued via helicopter. After he did not turn up at the trailhead a ground and air search were launched with five search parties on the ground as well as helicopter support. Apparently, the family’s children had “grown up in the outdoors” but by today’s standards that could mean anything in terms of their readiness to make a trek into the Selway-Bitterroot Wilderness. The father and three of his children had apparently been backpacking in the area previously and decided to take horses on this trek. The trail turned out to be more difficult and longer than they expected and the “horses began to struggle.” When one of the horses turned up lame, the 25-year-old son decided to go ahead on foot. He never showed up at Indian Lake, the evening rendezvous point for the group. When he did not show up the first evening, the party assumed he had walked out to the trailhead at Twin Lakes, some ten miles from Indian Lake. When he was not there a search was launched.
As I look at this scenario, it is evident it is the result of a great deal of human error and could have been prevented with a few very basic backcountry safeguards.
(1) Assuming that someone who had “grown up in the outdoors” knows how to navigate a wilderness area such as the Selway-Bitterroot is not a prudent assumption.
(2) Leaving your party alone without clothing or food is simply not a wise choice.
(3) The party leader, the father, did not make a wise choice when he allowed the party to separate.
(4) The trails in the Selway-Bitterroot are not well-maintained and have a lot of fallen trees and other obstacles which present challenges for stock, especially horses that are not seasoned to the backcountry. The party leader should have researched the trails and known these facts.
(5) What did the party have in the way of a GPS, topographic map, USFS maps? Although not well-maintained the trails are easy to follow. These basic navigational aids could have prevented this situation from happening and saved a lot of time, money, and grief for the family.
Basic Navigational Aids
For anyone going into the backcountry on horseback, whether hunting or not, the party should have the following basic navigational aids in addition to adequate pre-trip planning, research, and preparation.
- USFS map of the area to be travelled.
- GPS with appropriate maps and the ability to use the GPS.
- Topographic map of the area to be travelled, even if you have a GPS, onX app, or equal on a cell phone.
- Reserve battery or other means of charging a cell phone or GPS.
- Thorough assessment and research on the route you plan to take via USFS and other sources.
In today’s world with all of the navigational and safety devices we have available there is little reason to go into the backcountry without them. Garmin inReach will transmit real-time locations via tracks and waypoints using satellite communication technology. One of these units could have prevented the lost Utah horseman situation. InReach units have to have direct exposure to the sky and are easily attached to one’s person or saddle.
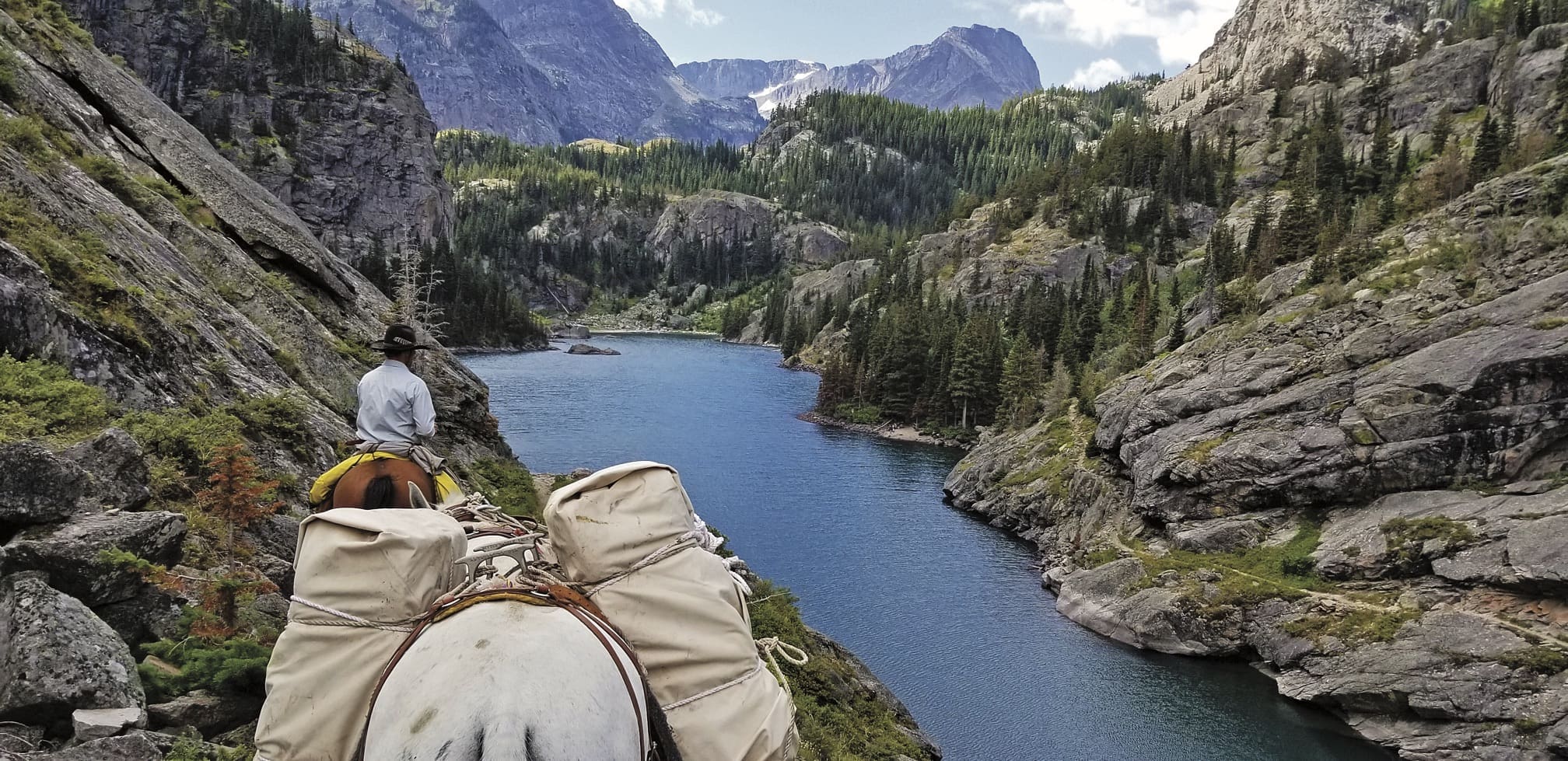
Stock in the Backcountry
From the previous scenario, it is evident that the party’s stock was likely not fit for the backcountry trek they chose. It is one thing to take day rides up and down well-maintained mountain trails. It is an entirely different situation to take stock into the backcountry where feed may be scarce, trails steep and challenging as well as significant trail obstructions and obstacles which may be encountered. Horses and mules need to be “seasoned” or “in shape” for the backcountry and be property shod and equipped with tack that is suited to the animals and the terrain. Taking a bunch of “dude” horses into the backcountry is often a good way to get into trouble and injure your stock.
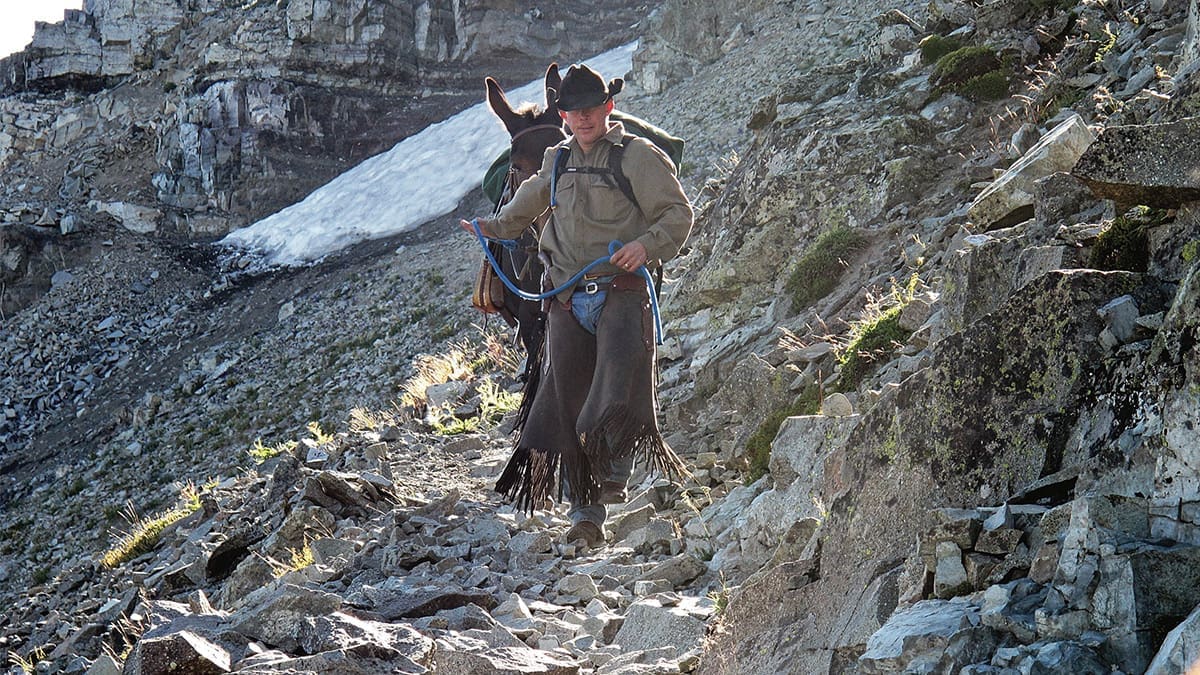

Many of the backcountry trails in Idaho, Montana, and Wyoming present difficult challenges in terms of a great deal of rock, steep grades, and treacherous obstacles, all of which present significant challenges for stock and humans alike. Before taking stock on the trails the stock needs to be conditioned, shod, and trained to handle difficult obstacles.
Maps and a Compass
Years ago, when I was just a beginner in the use of stock in the backcountry my primary means of exploring and scouting new areas was on foot, backpacking into remote areas in search of various big game habitats and the species that went along with the habitat. During this era, my efforts were guided by USFS maps, USGS 7 ½ minute topographic maps, and a compass. Once I found trails on maps that potentially would give me access to a key area, a great deal of effort was spent checking out these trails each summer to determine if they were maintained, or not. If they were not maintained perhaps they could be made passable with stock if I cleared fallen trees and other obstacles.
“Ground proofing” unknown USFS system trails or potential off-trail routes, including backpacking into and hunting the areas prior to attempting them with stock often requires a great deal of effort and perseverance.
It is always a good idea to check with the local regional office of the USFS or BLM when you are going to a place where you have not been before. I would specifically ask to talk with the person who runs the trail crew and walk the person through your route to note any changes, etc. Plan ahead as it may take a day or two to get to the right person. I have found that there is a wide range of information you will get from whoever answers the phone or gives you the information in a USFS office.
Finding Unknown Trails
The USFS updates maps on a fairly regular basis and many old trails which are no longer maintained are dropped from their map updates. I have found that if you can find copies of these old maps you may find a “treasure trove” of new and largely unknown access routes to key areas useful for hunting, but perhaps not useful any longer for current USFS travel routes. Often these trails can be made passable with stock by cutting out fallen trees and other obstacles, without violating any USFS policies related to cutting new trails or green trees.

Sometimes you can often learn about the location of these trails from USFS retirees or even regional offices, however, I have found that as time passes the current USFS employees are less and less familiar with what trail conditions may be like, even on well-used trails. The reason for this is simply because they do not get out on these trails as often as the old “brown shoe” forest officers once did. The other reason is money….and priorities how their time is spent. A less common source of old trail information is from old-time outfitters who may have used an area.
Off-Trail Navigation
As a hunter, I find that if you want to get away from the crowds or simply access key hunting areas you may have to navigate off-trail with your stock, either to a strategic campsite or a hunting area. More specifically, I like to find a remote and off-trail campsite that is located strategically providing easy access to a key hunting spot. For many years, in order to locate “off-trail” routes to areas that might hold elk, such routes had to be laid out on a USGS 7.5 minute topographic map, then checked on the ground, on foot, or horseback. Once I found likely “off-trail” areas I developed potential routes to these areas and often took my stock as far as I could go safely, camped, and perfected the route on foot as one would when laying out a logging road.

Topographic maps will often show areas of wooded cover, grassy slopes, wet areas, creeks as well as slope and elevation information. With a bit of insight and effort, you can lay out a tentative route with nothing more than these maps. Once you get out to the area to “ground proof” it a compass is often required to keep you on course. My experience surveying logging roads while working for the USFS as a summer job while going to college came in quite handy. USFS policies prohibit cutting out and establishing trails so these “off-trail” routes should take advantage of terrain and vegetation without the need to cut a new trail across the landscape.
Nearly 40 years ago I was so motivated to layout new routes for hunting trails each summer that I had a friend fly me over my hunting area in Idaho and I took photographs from his super cub of the areas where I was interested in planning new routes. Once I got the photos developed I drew with a “sharpie” the potential locations of the new routes. The next summer I matched the photos with my topographic maps and was able to link open meadows with pathways through the brush fields to access new hunting areas each summer.
Each new route had to be ground tested with my stock each summer to make sure it was navigable. In those days we had to remember the location of these trails as we traversed them in the summer. Fortunately, I had a riding horse whose memory was better than mine and once I got him to the starting point of such a trail he was “on it” to the end. It was interesting that when we traversed a route with our horses in the summer the elk would find these same trails and often, by fall, they had become elk highways.
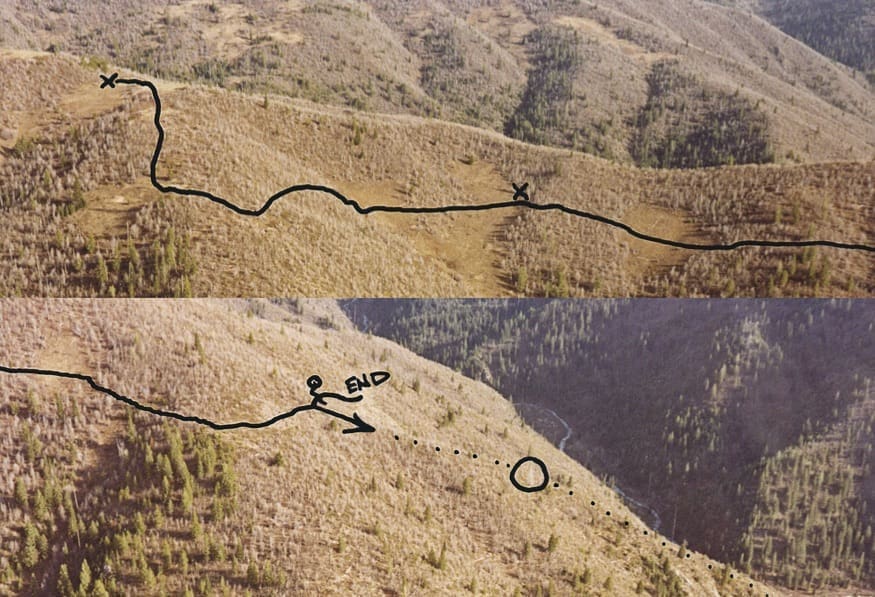

The above photographs were taken from an aircraft, printed, and off-trail routes were designed by hand to take advantage of open areas, topographical features, good soil, etc. to get riding and pack stock to new hunting areas. The “End” notation on the lower photo is where we initially tied our riding stock for the day as we dropped down the dotted route on foot to access bull elk across the canyon. Later we were able to take our stock all the way to the bottom of the canyon, cross, and go up the other side to pack out the bulls we accessed over the years via this route. This same technique can be facilitated today with Google Earth, onX Hunt, and other satellite imagery.
Today’s Technology
Today, with access to Google Earth, onX Hunt, and other mapping systems such as Garmin’s Bird’s Eye view, laying out a route and navigating that route with stock has taken on a whole new and much more interesting and simple dimension. These mapping systems and their route and tracking systems are a huge asset to the hunting horseman. In short, they have revolutionized the way in which today’s DIY hunter “scouts” a new hunting area and lays out routes to key spots. In addition, various states provide “hunt planners” complete with hunting unit maps, including georeferenced maps. Other sources of maps and information abound on the internet. Motorized and non-motorized trail use are especially important for the hunting horseman to steer clear of motorized routes. For example, Idaho State Parks and Recreation’s Trails.Idaho.gov app has excellent maps showing motorized and non-motorized trails. onX Hunt has a layer that shows recreational trails and identifies motorized and non-motorized trails.
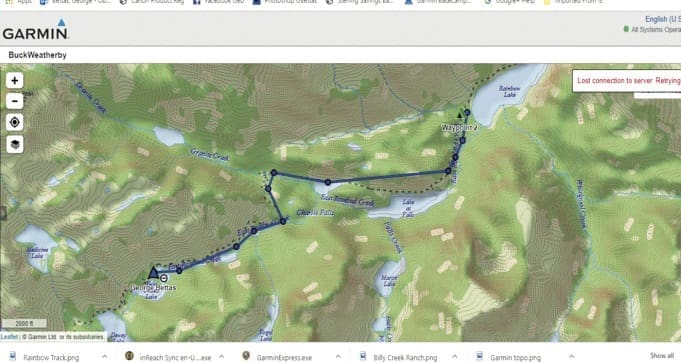
With Google Earth and other “satellite view” websites and smartphone apps, it is much easier to plan routes through all kinds of terrain where one can get riding and pack stock to key locations. With the ability to view 3-D images of a particular location along with satellite imagery it has become much easier to plan a tentative off-trail route since you have a virtual image of what the terrain actually is on the ground. White areas on a topographic map may be rock slides, whereas on Google Earth one can discern the difference between rockslide and grassy slopes, etc. onX Hunt has a line feature which one can use to lay out a route ahead of time and follow using the onX Hunt mapping feature and the satellite capabilities of a smartphone. Garmin GPS units have route planning features that allow one to plan a route ahead of time and then follow that route using GPS location information.
While you are negotiating a route you can record your actual track and use the track to navigate the route in the future. onX Hunt allows you to share routes and waypoints with others and Garmin GPS units with ‘share wirelessly’ capabilities allow you to share your waypoints and tracks with others in your hunting party. Garmin inReach allows a user to lay out routes ahead of time as well as share real-time locations and tracks with others while off the grid by communicating with others via email, text, or while off the grid (no cell coverage or wifi) from inReach unit to inReach unit. Google Earth has similar features for laying out routes, waypoints, and tracks. In addition to onX Hunt, inReach, and Google Earth, there are other excellent mapping apps for smartphones, including Avenza Maps, BaseMap, US topo maps, all of which have tracking, waypoint, and other features. If you are tech-savvy you can download a variety of USFS, USGS, satellite imagery, and other layers on your GPS, but that’s another story.
Once you have these routes, waypoints, and tracks on your GPS, inReach, or onX Hunt app on your cell phone it is simply a matter of using one of these units to navigate to where you want to go. In addition, I really like paper maps! As a result, I plot these tracks, routes, and waypoints on maps, such as custom topo maps from My Topo.
In a conversation with, onX Hunt Marketing Manager, he noted that most users of the onX products use them mostly to determine their location and property boundaries. Other features and layers of the onX smartphone apps and GPS chips are not used nearly as much. I found this interesting because the onX app and a Garmin GPS both have many other useful features which are valuable for negotiating the backcountry with stock. How many times have you been afield with someone who has a GPS and does not know how to use it? I have found that more often than not, many individuals who own a GPS do not know how to use it or do not know how to use most of its many features.
GPS features such as projecting a waypoint and then following the route through thick understory and timber is an invaluable feature for finding truly remarkable hunting areas.
onX Hunt (in this case using the topo map layer) allows the user to record a track that can later be followed to locate a kill site, develop a route for accessing a key area with stock or simply follow back to your point of origin.
GPS*
- Trip Computer – records the heading, time of day, elevation, distance traveled, elapsed time, etc.
- Altimeter – records total ascent, descent and elevation
- Map - shows location, property ownership (onX Hunt chip), track and distance travelled.
- Electronic compass – orientation to N, S, E, & W.
- Routing - laying out a route to travel ahead of time
- Waypoint Manager – waypoints you have recorded
- Share Wirelessly – allows user to share waypoints and tracks between GPS units with this feature
- Sight and Go- Allows user to project a waypoint in terms of distance and direction and then navigate to this projected waypoint. Especially useful if you shoot an elk across a big draw or canyon and need to navigate to it through thick trees, brush, etc.
*Note: Some GPS units may not have all of these features.
On X Hunt
- Map – shows location, elevation, property ownership, tracks, waypoints, line distance plus many other layers such as state lands, federal lands, recent fire activity, etc.
- Line Distance – I use this feature to lay out a route on the map which I can follow later in the field.
- Tracker - particularly useful for recording a track to or from a point or destination.
My Stock Always Comes First
When I first started this process nearly 50 years ago, I was quite timid in the use of what stock I either had or could borrow. This limited what areas I could access, but at least I did not injure any of my stock attempting to go places where I should not have gone. It was always better to ride my horse part of the way to a key spot and walk the rest of the way. Later, as I experienced other hunters using horses I experienced a number of overly bold hunters regularly put their horses or mules in extremely dangerous situations and did not think anything about it.
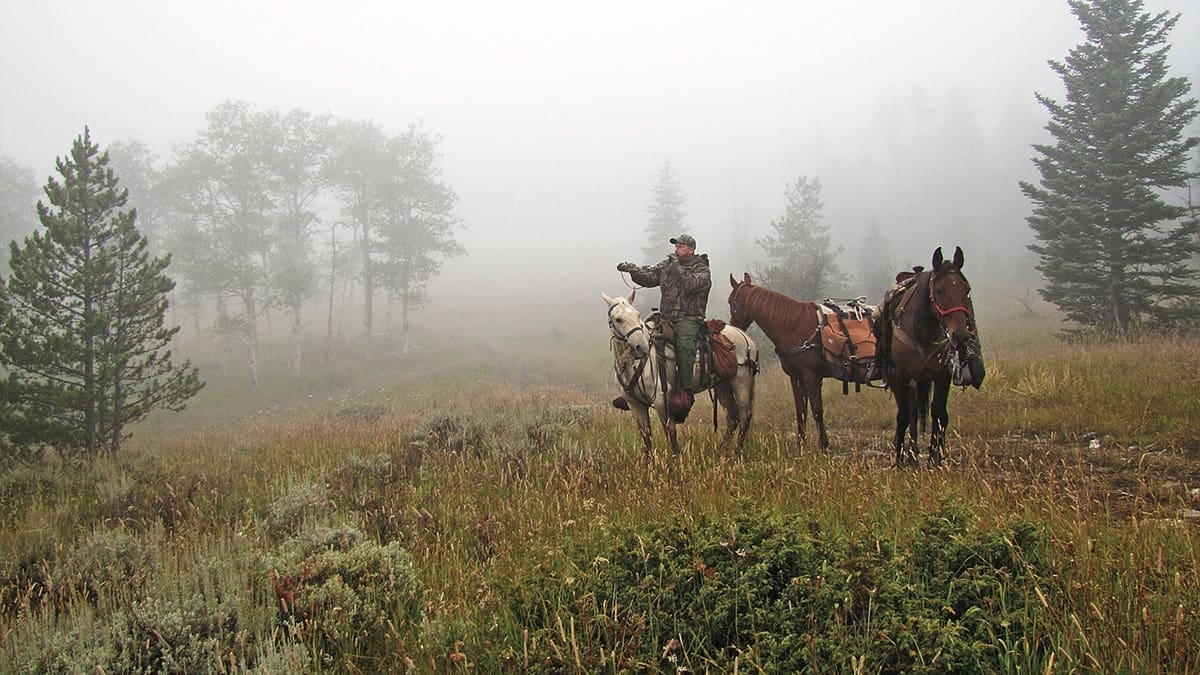

These individuals injured or killed good riding and pack animals by being overly bold and uncaring. They had a lot of money and “it was just a horse or mule.” Often these animals stood in a pasture 11 months of the year, got shod, and were put out into the backcountry regardless of their conditioning, age, or anything else. Personally, I learned long ago that my horses and my mules are my hunting partners and the last thing I want to do is put them in harm’s way. Hunting elk without my stock is like hunting birds without a bird dog….it is truly a shared experience and one that I will always treasure.
My hunting partners share my affection for their stock and when presented with treacherous or otherwise dangerous trail or route conditions their stock comes first, regardless of how far they may have to walk or lead a single animal or pack string to safely navigate the route.













